Source: https://medium.com/@containeroo/traefik-2-0-route-external-services-through-traefik-7bf2d56b1057
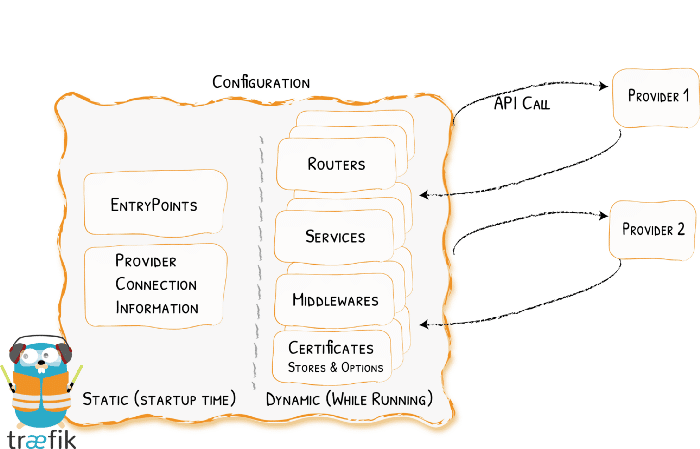
Introduction
In this tutorial we will show you how you can route non-Docker services through Traefik.
Let’s suppose you want to access your Pi-hole admin console (http://192.168.0.10:80/admin) by browsing to pihole.example.com.
Prerequisites
You have read our other articles:
and you use this Traefik configuration.
Make sure you configure in the providers section of your /opt/traefik/data/traefik.yml an external configuration file /config.yml.
providers:
docker:
endpoint: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
exposedByDefault: false
file:
filename: /config.ymlSetup config.yml
Edit /opt/containers/traefik/data/config.yml and create a new router pihole:
http:
routers:
pihole:
entryPoints:
- "https"
rule: "Host(`pihole.example.com`)"
middlewares:
- addprefix-pihole
tls:
certResolver: http
service: piholeStill in /opt/containers/traefik/data/config.yml create a service for the new router:
services:
pihole:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: "http://192.168.0.10:80"
passHostHeader: trueBecause the admin panel of Pi-hole is only reachable at the path /admin, you have to create an additional middleware (also in /opt/containers/traefik/data/config.yml):
middlewares:
addprefix-pihole:
addPrefix:
prefix: "/admin"If you have configured Traefik as we’ve described in the advanced tutorial, your config.yml should now look like this:
http:
routers:
pihole:
entryPoints:
- "https"
rule: "Host(`pihole.example.com`)"
middlewares:
- default-headers
- addprefix-pihole
tls:
certResolver: http
service: pihole
services:
pihole:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: "http://192.168.0.10:80"
passHostHeader: true
middlewares:
addprefix-pihole:
addPrefix:
prefix: "/admin"
https-redirect:
redirectScheme:
scheme: https
default-headers:
headers:
frameDeny: true
sslRedirect: true
browserXssFilter: true
contentTypeNosniff: true
forceSTSHeader: true
stsIncludeSubdomains: true
stsPreload: true
default-whitelist:
ipWhiteList:
sourceRange:
- "10.0.0.0/24"
- "192.168.0.0/16"
- "172.0.0.0/8"
secured:
chain:
middlewares:
- default-whitelist
- default-headersWe also added the middleware default-headers to the new pihole router.
Don’t forget to restart Traefik docker restart traefik to reload the new config.yml!
Wildcard certificates
If you use a wildcard certificate as described in this article, you must leave the tls section empty {}:
http:
routers:
pihole:
entryPoints:
- "https"
rule: "Host(`pihole.example.com`)"
middlewares:
- default-headers
- addprefix-pihole
tls: {}
service: piholeBonus example
Here you can find a complete config.yml to route a Synology Diskstation and Pi-hole through Traefik.
http:
routers:
pihole:
entryPoints:
- "https"
rule: "Host(`pihole.example.com`)"
middlewares:
- default-headers
- addprefix-pihole
tls:
certResolver: http
service: pihole
synology:
entryPoints:
- "https"
rule: "Host(`synology.example.com`)"
middlewares:
- default-headers
tls:
certResolver: http
service: synology
services:
pihole:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: "http://192.168.0.10:80"
passHostHeader: true
synology:
loadBalancer:
servers:
- url: "http://192.168.0.11:5000"
passHostHeader: true
middlewares:
addprefix-pihole:
addPrefix:
prefix: "/admin"
https-redirect:
redirectScheme:
scheme: https
default-headers:
headers:
frameDeny: true
sslRedirect: true
browserXssFilter: true
contentTypeNosniff: true
forceSTSHeader: true
stsIncludeSubdomains: true
stsPreload: true
default-whitelist:
ipWhiteList:
sourceRange:
- "10.0.0.0/24"
- "192.168.0.0/16"
- "172.0.0.0/8"
secured:
chain:
middlewares:
- default-whitelist
- default-headersAs you can see, the Synology router has no extra middleware, because a Synology Disksation is accessible without any additional path.